Domestic semiconductor production boosted through tax incentives

Anúncios
Domestic semiconductor production is boosted through tax incentives that encourage local manufacturing, stimulate innovation, and enhance supply chain stability, while also presenting challenges such as regulatory compliance and talent acquisition.
Domestic semiconductor production boosted through tax incentives is more than just a policy shift; it’s a potential game changer. Ever thought about how these incentives might reshape our tech landscape? Let’s dive in and explore the possibilities.
Anúncios
Understanding tax incentives for semiconductor production
Understanding the role of tax incentives in semiconductor production is crucial for grasping how industries evolve and thrive. These financial advantages are designed to encourage companies to invest in domestic manufacturing. By easing the financial burdens, governments can stimulate growth in an essential sector. Let’s delve deeper into how these incentives function.
What Are Tax Incentives?
Tax incentives are benefits that reduce the amount of tax a business owes. They can come in various forms, including credits, deductions, and exemptions. Such incentives not only help businesses save money but also encourage them to expand operations.
Anúncios
Benefits for Semiconductor Companies
The advantages of these incentives are numerous for semiconductor companies. They can:
- Lower production costs, making manufacturing more competitive.
- Encourage investment in advanced technologies and research.
- Create jobs and boost local economies.
Furthermore, these incentives foster a favorable environment for innovation. Companies can allocate more resources to research and development, which is essential in a fast-evolving industry like semiconductors.
The Impact on Domestic Markets
As domestic production is boosted through these incentives, the overall supply chain also benefits. With more manufacturers operating locally, there is decreased reliance on foreign suppliers. This shift enhances national security and stabilizes product availability.
It’s interesting to note that governments often tie these incentives to specific requirements, such as production milestones or job creation goals. This ensures that the benefits translate into tangible outcomes for the economy.
Challenges Associated with Tax Incentives
While tax incentives can drive growth, there are challenges to consider. Some companies may exploit these incentives without making significant contributions to the local economy. Therefore, it’s vital for legislatures to monitor and enforce guidelines.
Overall, understanding tax incentives is key to appreciating how they push semiconductor production forward, ensuring competitiveness and innovation within the industry.
The impact on domestic supply chains
The impact of tax incentives on domestic supply chains is significant. These incentives can reshape how businesses operate, especially in the semiconductor industry. By reducing costs and encouraging local production, companies can streamline their processes and improve efficiency.
Strengthening Local Supply Chains
When semiconductor manufacturers receive tax incentives, they often invest in local facilities and resources. This investment leads to:
- Shorter delivery times due to reduced dependence on overseas suppliers.
- Increased reliability and flexibility in production schedules.
- Enhanced collaboration between local suppliers and manufacturers.
Such improvements can lead to a stronger domestic economy, as businesses thrive when they can rely on nearby partners and resources.
Reducing Vulnerabilities
Domestic supply chains often face less risk from global events, such as political instability or natural disasters. By boosting local production through tax incentives, companies can minimize disruptions in their supply chains. A robust domestic presence ensures that businesses can adapt to market changes quickly.
Moreover, companies are likely to see reduced transportation costs. Lower costs lead to higher profit margins, which can then be reinvested into other areas of the business.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
The shift towards local production generates jobs, which stimulates economic growth. As semiconductor companies expand their facilities and hire more workers, local communities benefit from increased employment opportunities.
These developments create a ripple effect, as new jobs lead to heightened consumer spending, further driving local economies. With more people employed, demand for products and services rises, contributing to overall economic health.
How tax incentives promote innovation in technology
Tax incentives play a vital role in driving innovation within the technology sector, particularly in semiconductor production. By reducing financial burdens, these incentives allow companies to allocate more resources toward research and development. This focus on innovation helps businesses stay ahead in a competitive market.
Encouraging Investment in R&D
When companies receive tax incentives, they often invest more in developing new technologies. These investments can take various forms:
- Funding for experimental projects and prototypes.
- Collaboration with universities and research institutions.
- Acquisition of advanced equipment and technologies.
Such investments lead to breakthrough innovations that can revolutionize industries and improve production processes.
Attracting Talented Workforce
By promoting innovation, tax incentives help attract skilled workers to the semiconductor industry. As companies innovate, there is a greater demand for talent in fields like engineering and computer science. This influx of talent not only enhances the company’s capabilities but also fuels further innovation.
When workers see an industry committed to growth and new ideas, they are more likely to join and contribute to its success. The collaboration between skilled professionals creates an environment where ideas can flourish.
Boosting Competitiveness
As more companies innovate, the overall competitiveness of the industry increases. This progress leads to higher quality products being produced at lower costs. Customers benefit as they have access to superior technology and services.
Moreover, with a focus on innovation, companies can differentiate themselves in the marketplace. By leveraging tax incentives, they are encouraged to continuously evolve their offerings, ensuring they meet changing consumer demands effectively.
Challenges and considerations for semiconductor companies
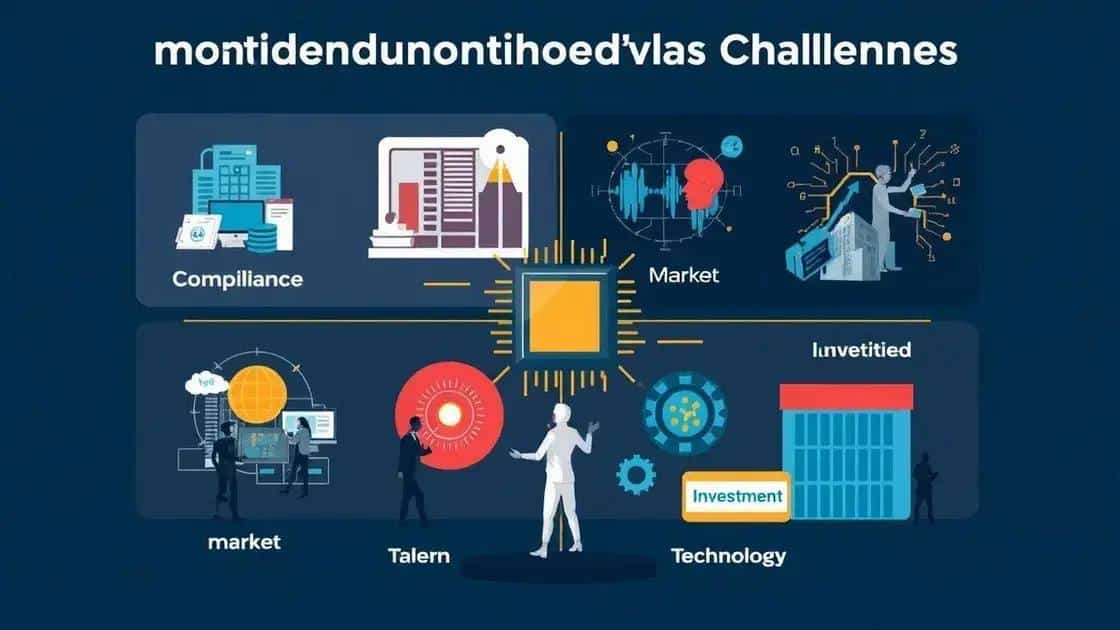
Challenges and considerations for semiconductor companies in the context of tax incentives are critical to understand. While these incentives can boost growth, they also come with potential hurdles that companies must navigate.
Compliance with Regulations
One major challenge is ensuring compliance with regulations attached to tax incentives. Companies need to maintain accurate records and meet specific requirements to qualify for these benefits. This might involve stringent reporting and audits, which can be time-consuming.
Market Volatility
Semiconductor companies also face market volatility, which can impact their ability to leverage tax incentives effectively. Factors such as supply chain disruptions, global demand fluctuations, and changes in technology can challenge strategic planning.
In addition, fluctuations in the market can make it challenging to predict future revenues. If a company invests significantly based on anticipated incentives and market conditions shift, they may face financial struggles.
Competition for Talent
Another consideration is the competition for skilled labor. As more companies invest in semiconductor production, the demand for qualified professionals increases. Organizations must offer competitive salaries and benefits to attract top talent.
This competition not only drives up labor costs but also makes it harder for smaller companies to compete with larger firms that may have more resources.
Investment in Technology
Investing in advanced technologies is essential to remaining competitive in the semiconductor industry. However, the high cost of cutting-edge equipment can be a barrier for companies, especially smaller ones. Even with tax incentives, companies need to weigh the risks and benefits of such investments carefully.
Overall, while tax incentives present a unique opportunity for semiconductor companies, understanding these challenges is crucial for long-term success. Proper planning and strategic foresight can help companies navigate these waters effectively.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Domestic Semiconductor Production and Tax Incentives
What are tax incentives for semiconductor companies?
Tax incentives are financial benefits provided by the government to encourage semiconductor companies to invest in local manufacturing and innovation.
How do tax incentives affect domestic supply chains?
Tax incentives strengthen domestic supply chains by promoting local production, reducing reliance on foreign suppliers, and enhancing efficiency.
What challenges do semiconductor companies face with tax incentives?
Companies must navigate regulatory compliance, market volatility, and competition for skilled labor while leveraging tax incentives.
How do tax incentives promote innovation in technology?
These incentives encourage companies to invest in research and development, driving advancements and helping them stay competitive in the market.





